摘要:
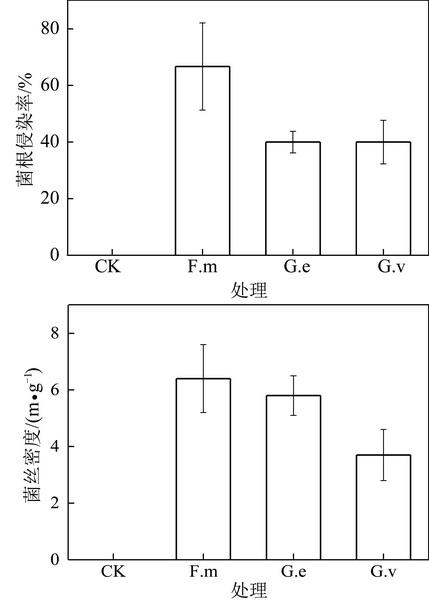
呼伦贝尔草原区露天煤矿开采会造成大面积土壤和植被的损毁,恢复难度较大。丛枝菌根真菌可以与80%以上的高等植物形成菌根共生体,能促进植被的生长,加速矿区植被恢复。以黄花苜蓿为供试植物,通过温室盆栽模拟实验,研究了在土壤灭菌条件下接种3种丛枝菌根真菌即摩西管柄囊霉(Funneliformis mosseae,简称F.m)、幼套球囊霉(Glomus etunicatum,简称G.e)、地表球囊霉(Glomus versiforme,简称G.v)对黄花苜蓿幼苗根系菌根侵染率、根外菌丝密度、植株生长及其生理、营养状况的影响。结果表明:3种接菌处理均可与黄花苜蓿形成良好的共生关系,不同菌种与宿主植物的亲和程度存在差异。与对照处理相比,3种接菌处理均显著提高了植物株高(9.9%~23.5%)和叶色值(17.6%~21.0%)。接种F.m显著增加了植株地上和根系生物量、叶片可溶性蛋白、净光合速率、蒸腾速率和气孔导度及根系P含量。接种G.e显著提高了地上生物量、叶片可溶性蛋白、蒸腾速率、植株地上和根系P含量。相关分析结果表明,菌根侵染率与植物生物量、叶片可溶性蛋白、气孔导度、地上部分N质量分数呈显著相关,与根外菌丝密度、株高、蒸腾速率、根系P质量分数呈极显著相关,菌根侵染率、根外菌丝密度与植物生长、生理及营养状况之间存在协同效应。3种接菌处理对黄花苜蓿幼苗生长均有不同程度的促进作用,其中以摩西管柄囊霉的效果最好,幼套球囊霉次之,地表球囊霉效果最差。
Abstract:
Opencast coal mining in Hulun Buir grassland area has resulted in a large destruction of land and vegeta- tion,and the ecological reclamation is difficulty. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can form mycorrhizal symbiosis with more than 80% of higher plants,which can promote the growth of vegetation and accelerate the vegetation restoration in mining areas. With yellow flower alfalfa as the test material,the effects of three kinds of arbuscular mycorrhizal (Funneliformis mosseae,Glomus etunicatum,Glomus versiforme) inoculation on the plant infection rate,the growth, physiological and nutritional characteristics, and soil mycelium density in the opencast mining area were studied through pot experiment in the greenhouse. The results showed that all three strains could form a good symbiotic relationship with yellow flower alfalfa,and the degree of affinity between different strains and host plants was different. Compared with CK treatment,plant height and SPAD value in the three inoculated treatments were significantly in- creased,which the plant height increased by 9. 9% to 23. 5% ,and SPAD increased by 17. 6% to 21. 0% . Inoculation of Funneliformis mosseae significantly increased plant aboveground biomass and root biomass,leaf soluble protein con- tent,and plant leaf net photosynthetic rate,transpiration rate,stomatal conductance and root phosphorus concentration. Inoculation of Glomus etunicatum significantly increased plant aboveground biomass,leaf soluble protein content,tran- spiration rate,and plant aboveground and root phosphorus concentration. Correlation analysis indicated that the mycor- rhizal infection rate was correlated with biomass,leaf soluble protein,stomatal conductance,the ground part N concen- tration,and also significantly correlated with hyphal density,transpiration rate,plant height,root system P concentra- tion. There was a synergistic effect between mycorrhizal infection rate,hyphal density and plant growth,physiological, and nutritional status. The three strains of inoculation had different degrees of promoting effect on the growth of yellow flower alfalfa seedlings,among which Funneliformis mosseae was the best,Glomus etunicatum was the second,Glomus versiforme was the worst.




 下载:
下载:


